THE HIDDEN TAX OF POOR RISK MANAGEMENT
Your business is leaking money. Not in the obvious ways — like overspending or inefficiency — but in silent, insidious drains you might not even see. Poor risk management isn’t just about avoiding disasters; it’s a profit killer, a growth stifler, and, in the worst cases, an executioner of businesses that could have thrived.

Consider this: 30% of bankruptcies are due to operational failures that could have been mitigated with better risk practices (OECD). That’s not bad luck—it’s self-inflicted. And if you think your company is immune, think again.
- This isn’t theoretical. Every day, businesses hemorrhage cash through:
- Uncontrolled operational risks —process failures, supply chain disruptions, compliance fines.
- Strategic blind spots —missed opportunities, reputational damage, eroded customer trust.
- Employee disengagement —teams that don’t see risk as their problem, costing you in errors, delays, and lost innovation.
The result? Lower profitability. Stunted growth. And, in extreme cases, extinction.
But here’s the good news: this is entirely optional and fixable.
In this e-book, we’ll expose the 12 most damaging costs of poor risk management —many of which you’re likely paying right now — and deliver 12 actionable solutions to turn risk from a liability into a competitive advantage. You’ll learn how to:
- Engage every employee in risk ownership (not just compliance, but profit protection).
- Stop financial bleed from preventable failures.
- Turn risk-aware decision-making into a growth engine.
This isn’t another dry risk management manual. This is a survival guide for profitable, resilient business leadership.
Ready to plug the leaks? Let’s begin.
🚨 YOUR BUSINESS IS LEAKING £££ – FIND THE HOLES! 🚨
83% of UK SMEs lose £50k+ yearly from hidden risks they don’t even measure:
❌ Operational failures burning cash
❌ Supply chain disasters killing margins
❌ Cyberattacks costing millions
BusinessRiskTV’s NEW eBook reveals:
✅ 12 PROVEN FIXES to stop profit leaks
✅ Real case studies from UK businesses
✅ Simple checklists to act TODAY
🔥 Stop the bleed—before it’s too late!
#BusinessRisk #ProfitProtection #SMEs #RiskManagement
—
Chapter 1: The Hidden Costs of Poor Risk Management – How Ignoring Risk Erodes Your Profits and Threatens Survival
Introduction: The Silent Profit Killer
Every business faces risks—some obvious, others invisible. But when risk management is an afterthought, those risks don’t just linger; they multiply costs, shrink margins, and sabotage growth. This chapter exposes the real financial and operational toll of poor risk management—and why most businesses underestimate it.
—
1. The Direct Financial Costs: Where the Money Leaks
A. Unexpected Losses from Operational Failures
- Example: A manufacturing firm ignores equipment maintenance, leading to a breakdown that halts production for 48 hours. The result? £250,000 in lost revenue + £50,000 in emergency repairs.
- Stat: Companies with weak operational risk management see 30% higher unexpected costs (Deloitte).
B. Regulatory Fines & Legal Penalties
- Case Study: A UK SME in financial services fails to comply with GDPR, resulting in a £180,000 fine —plus reputational damage.
- Stat: 60% of small UK businesses aren’t fully compliant with key regulations (FSB).
C. Insurance Premiums & Uncovered Losses
- Poor risk controls = higher premiums (or worse, insurers refusing coverage).
- Example: A restaurant without proper fire safety measures faces doubled insurance costs after a minor kitchen fire.
—
2. The Indirect Costs: What You’re Not Measuring (But Should Be)
A. Lost Productivity & Employee Burnout
- Scenario: A retail chain’s poor inventory risk management leads to constant stock shortages. Staff waste 15 hours/week handling complaints and manual fixes.
- Stat: Disengaged employees cost UK businesses £340 billion annually (Gallup).
B. Reputation Damage & Customer Attrition
- Case Study: A data breach at a UK e-commerce firm loses 20% of its customers within 6 months — recovery costs: £500k+ in marketing.
- Stat: 88% of consumers hesitate to buy after a security incident (PwC).
C. Missed Opportunities & Stunted Growth
- Example: A tech startup avoids expanding to Europe due to fear of unmanaged risks — competitors seize the market, costing £2M+ in lost revenue.
—
3. The Survival Threat: When Poor Risk Management Becomes Existential
A. Cash Flow Crises
- Small risks compound: A construction firm’s unpaid invoices (credit risk) + a delayed project (operational risk) = insolvency within 90 days.
- Stat: 82% of UK business failures cite cash flow issues (Insolvency Service).
B. Investor & Lender Distrust
- Scenario: A startup’s repeated risk failures scare off venture capital – funding round collapses.
- Stat: 70% of investors demand robust risk frameworks before backing a business (EY).
C. The Final Cost: Business Collapse
- Real-Life Example: £7B collapse was rooted in systemic risk blindness —ignoring contract risks, debt, and supply chain failures.
—
4. Why Businesses Underestimate Risk (Until It’s Too Late)
- “It won’t happen to us” bias
- Firefighting culture (reacting to risks, not preventing them)
- Misaligned incentives (short-term profits > long-term resilience)
—
5. The Bottom Line: What Poor Risk Management Really Costs You
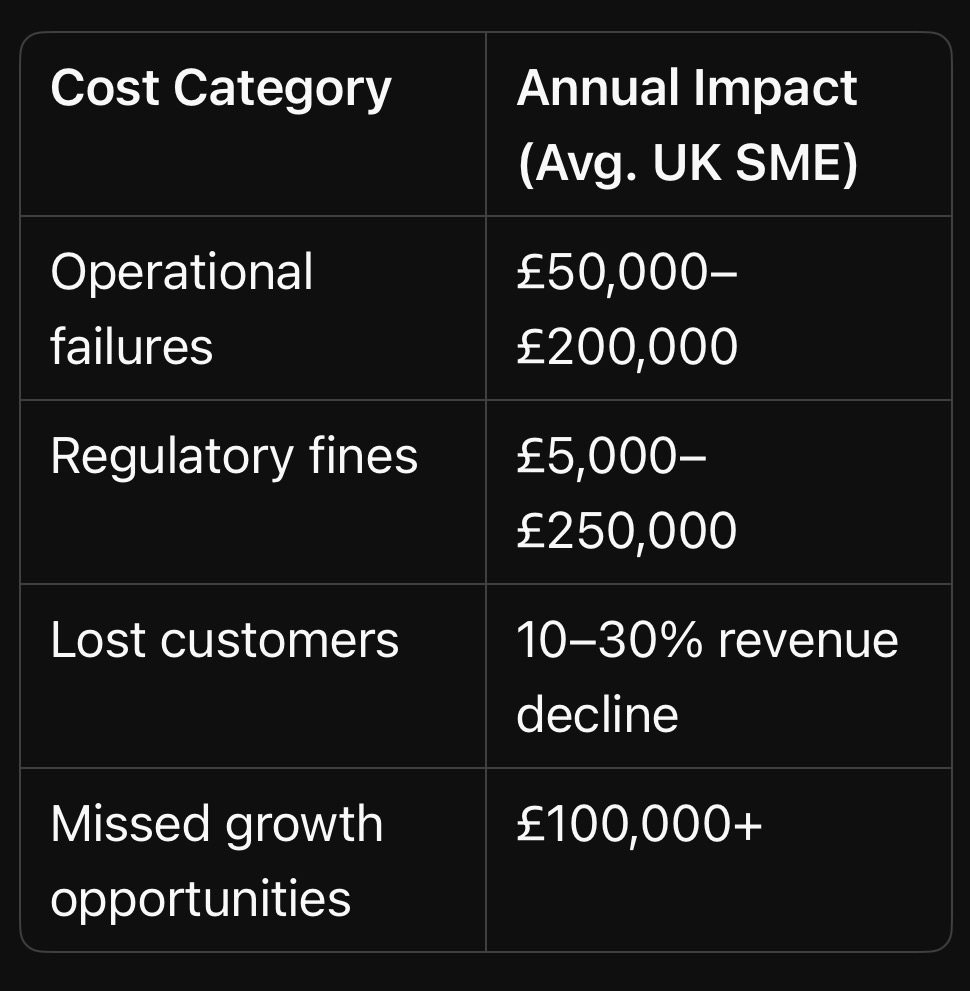
Key Takeaway: Poor risk management isn’t just about avoiding disasters — it’s a tax on profitability, growth, and survival.
—
Actionable Insight: Audit one high-cost risk in your business this week (e.g., late payments, compliance gaps). What’s it really costing you?*
—
Chapter 2: The True Cost of Operational Failures – How Inefficient Risk Management Cripples Your Business
Introduction: The Domino Effect of Poor Operational Risk Controls
Operational risks don’t just cause one-off incidents—they trigger chain reactions that drain cash, demoralise teams, and erode customer trust. This chapter exposes the hidden, cascading costs of mismanaged operational risks and why most businesses only see the tip of the iceberg.
—
1. The Obvious Costs: What You Can’t Ignore
A. Downtime & Lost Production
- Manufacturing Example: A single machine failure halts a production line for 8 hours → £25,000 in lost output + overtime costs to catch up.
- Hospitality Example: A restaurant’s refrigeration breakdown spoils £3,000 of stock overnight — plus angry customers.
- Stat: UK manufacturers lose £180 billion/year to unplanned downtime (EEF).
B. Emergency Repairs & Rush Orders
- Reactive spending costs 3–5X more than planned maintenance.
- Case Study: A logistics firm ignores fleet maintenance → two vans fail MOTs simultaneously → £8k in last-minute rentals + delayed deliveries.
C. Waste & Rework
- Construction Example: Poor quality control leads to £50,000 of defective materials — then doubles labour costs to fix errors.
- Stat: 20–30% of project budgets are wasted on rework (KPMG).
—
2. The Hidden Costs: What You’re Not Tracking (But Should Be)
A. Employee Productivity Drain
- Scenario: A retail store’s outdated inventory system causes daily stock discrepancies. Staff waste 4 hours/day manually reconciling data instead of selling.
- Stat: UK workers spend 15% of their time fixing preventable issues (PwC).
B. Management Distraction & Burnout
- Small Business Reality: The owner spends 60% of their week putting out fires (supplier delays, IT crashes) instead of growing the business.
- Psychological Cost: Chronic stress → poor decisions → more risks.
C. Customer Churn & Reputation Erosion
- E-commerce Example: A fulfilment centre’s picking errors lead to 10% of orders arriving wrong → 15% of customers never return.
- Stat: 70% of customers switch brands after just 2–3 bad experiences (Salesforce).
—
3. The Strategic Costs: How Operational Risks Stunt Growth
A. Lost Competitive Advantage
- Case Study: A UK bakery’s unreliable oven delays a product launch by 3 months —competitors dominate supermarket shelves first.
B. Innovation Paralysis
- Teams stuck in “firefighting mode” never test new ideas.
- Example: A tech firm’s IT team spends 80% of time fixing outages → zero R&D progress.
C. Investor & Partner Distrust
- Supply Chain Example: A fashion brand’s repeated delivery failures lead to two major retailers dropping them —£500k annual revenue gone.
—
4. The Survival Threat: When Operational Risks Become Fatal
A. Cash Flow Death Spiral
- Construction Firm Case Study:
1. Poor contract risk assessment → unpaid invoices pile up
2. Equipment breakdown → project delays
3. Penalties for late delivery → bank calls in loan
Result: Administration within 6 months.
B. The Carillion Effect
- How ignoring operational risks (contract mismanagement, cash flow gaps) led to the UK’s biggest corporate collapse.
—
5. The Bottom Line: Quantifying Operational Risk Costs
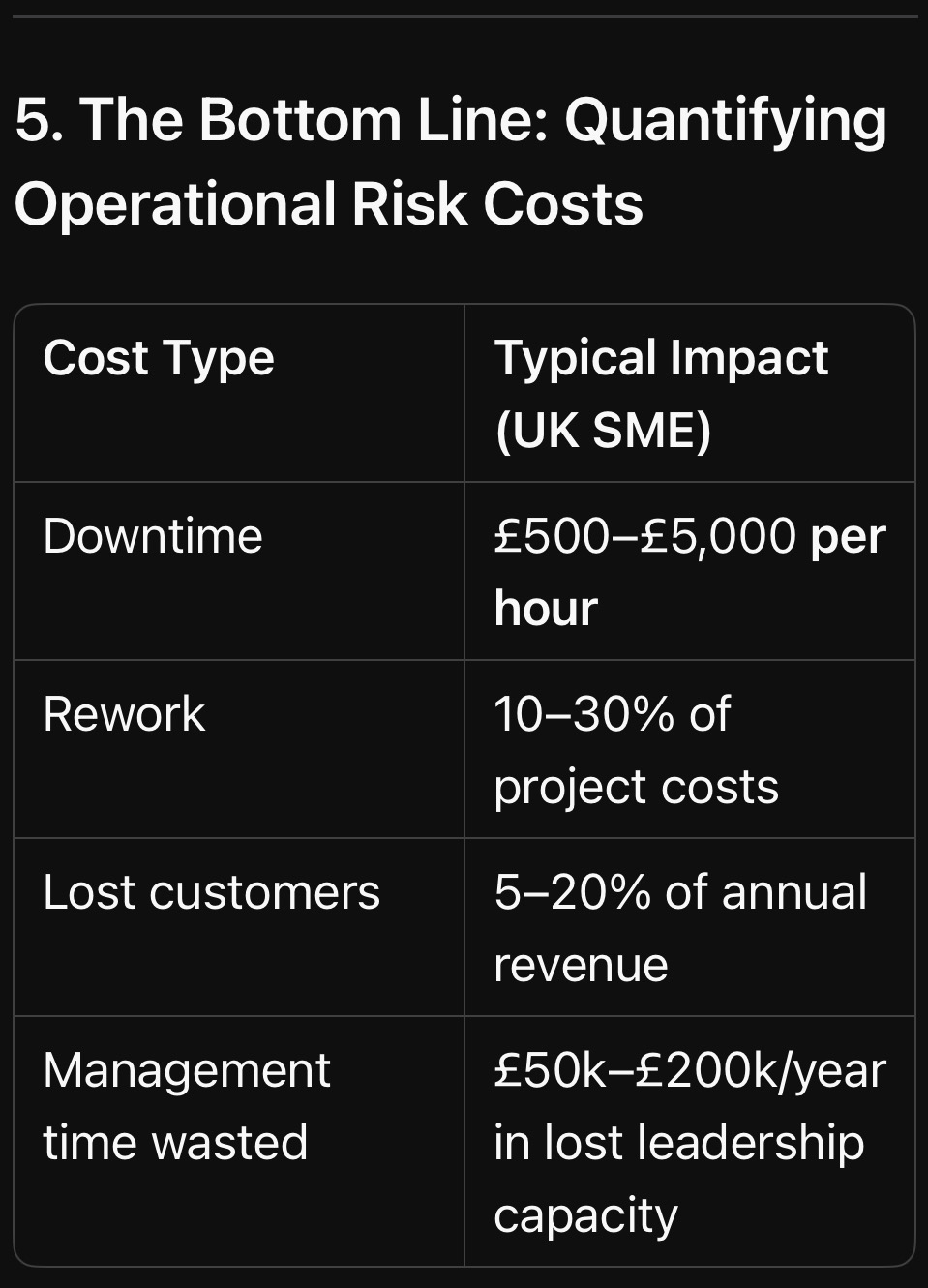
Key Insight: Operational risks don’t just cost money—they steal time, talent, and future opportunities.
—
More From BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub : How to Fix It
We explore how to turn operational risk management into a profit centre, including:
- The 5-minute daily habit that prevents 80% of failures
- How to engage frontline teams in risk reduction (with real-world examples)
Actionable Task: Map one critical operational process (e.g., order fulfilment). Where could a single failure cost you £10k+?
—
Chapter 3: Strategic Risks – How Blind Spots in Planning Can Bankrupt Even Profitable Businesses
Introduction: The Silent Assassin of Business Growth
Strategic risks don’t announce themselves with alarms — they creep in unnoticed while leadership is distracted by day-to-day operations. By the time the damage is visible, it’s often too late to pivot. This chapter exposes how poor strategic risk management destroys market position, erodes competitive edge, and turns industry leaders into cautionary tales.
—
1. What Are Strategic Risks? (And Why They’re Different)
Strategic risks stem from:
- Poor market foresight (e.g., Blockbuster ignoring streaming)
- Flawed business models (e.g., Toys “R” Us failing to adapt to e-commerce)
- Disruptive competitors (e.g., Uber vs. traditional taxis)
- Regulatory shifts (e.g., GDPR crushing non-compliant firms)
Key Difference: Unlike operational risks (which drain cash), strategic risks threaten your entire reason for existing.
—
2. The Direct Costs of Strategic Missteps
A. Missed Market Shifts = Lost Revenue
- Case Study: Kodak invented the digital camera but feared cannibalising film sales. By the time it pivoted, competitors dominated. Result: Bankruptcy.
- Stat: 52% of Fortune 500 companies since 2000 have disappeared due to strategic failures (Accenture).
B. Failed Expansions & Wasted R&D
- Example: A UK retailer expands into Europe without assessing local demand. £2M in setup costs → stores close within 18 months.
- Stat: 70% of corporate transformations fail (McKinsey), often due to poor risk assessment.
C. Reputation Collapse from Strategic Blunders
- BP’s Deepwater Horizon wasn’t just an operational accident—it was a strategic failure in risk culture, costing $65B+.
—
3. The Hidden Costs: Invisible Erosion of Value
A. Investor Flight & Lower Valuations
- Scenario: A tech firm’s CEO dismisses AI as a “fad.” Investors shift funds to AI-driven rivals. Share price drops 40% in a year.
- Stat: Companies with weak strategic risk management trade at 15–20% lower valuations (Harvard Business Review).
B. Talent Drain & Leadership Crises
- Top talent leaves stagnant companies.
- Example: A traditional bank loses its best fintech minds to startups after refusing to innovate.
C. Supplier & Partner Defections
- Case Study: A car manufacturer’s slow EV transition leads key suppliers to prioritise Tesla. Suddenly, parts cost 20% more.
—
4. The Ultimate Cost: Business Obsolescence
A. The “Blockbuster Effect”
- Not just “bad luck” — a failure to scenario-plan for streaming.
- Lesson: If your strategy doesn’t include “What if we’re wrong?“, you’re gambling.
B. The UK High Street Bloodbath
- Maplin, BHS, Debenhams: All had revenue—but no strategy for digital/experiential shifts.
C. The Startups That Scale Into Failure
- WeWork’s $47B Meltdown: A business model risk (long-term leases vs. short-term rentals) disguised as growth.
—
5. Why Businesses Miss Strategic Risks
- “Success blindness” (past performance ≠ future proof)
- Overconfidence in data (ignoring weak signals)
- Boardrooms detached from market realities
—
6. The Bottom Line: What Strategic Risks Cost You
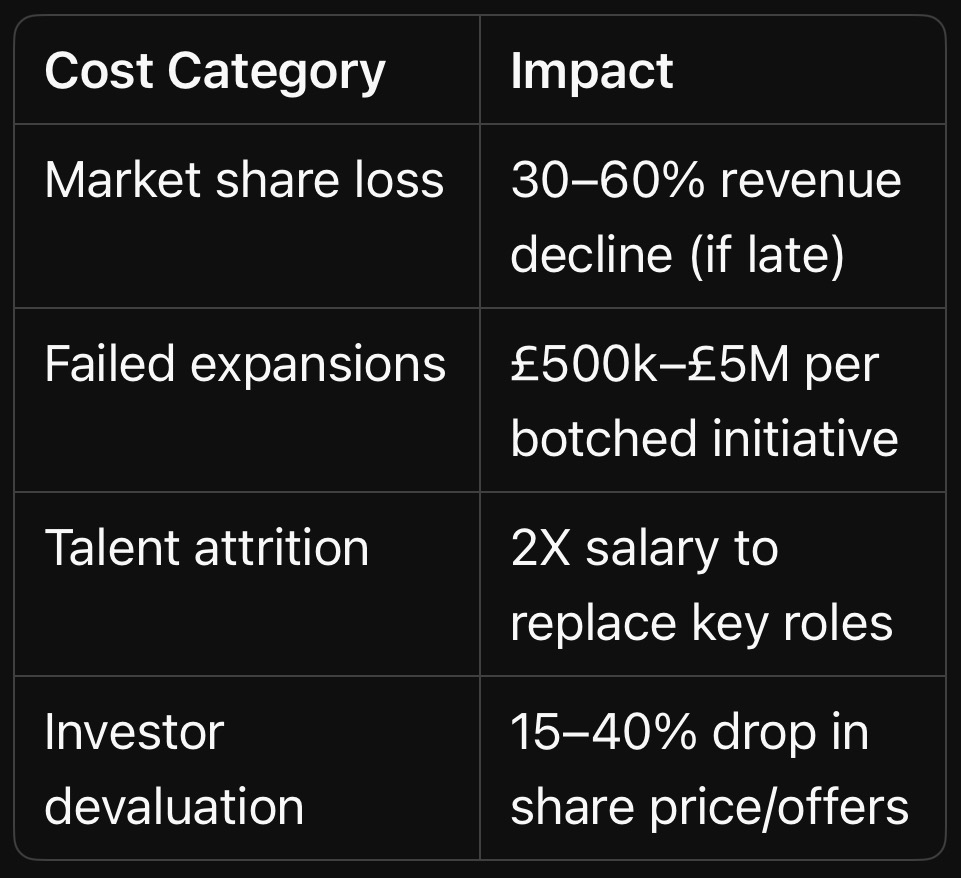
Key Takeaway: Strategic risks don’t just hurt profits — they erase entire business models.
—
More from BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub : How to Anticipate & Outmanoeuvre Strategic Risks
We explore practical frameworks to:
- Spot industry shifts early (using weak signals)
- Stress-test your strategy against disruption
- Turn risks into opportunities (like Amazon’s pivot from books to cloud)
Actionable Task: List one strategic assumption your business relies on (e.g., “Customers will always prefer X”). How would you survive if it’s wrong?
—
Chapter 4: Financial Risks – How Poor Cash Flow & Debt Management Can Sink Your Business Overnight
Introduction: The Silent Killer of Healthy Businesses
Profit doesn’t equal survival. Thousands of UK businesses post record revenues—right before going bust. Why? Because financial risk management isn’t about counting pennies — it’s about anticipating traps that strangle cash flow, trigger defaults, and collapse supply chains.
This chapter exposes the lethal financial risks hiding in plain sight — and why even profitable companies run out of money.
—
1. The Obvious (But Ignored) Financial Risks
A. Cash Flow Crises – The #1 Business Killer
- Reality: 82% of UK business failures cite cash flow problems as the primary cause (UK Insolvency Service).
- Example: A £5M-turnover construction firm collapses because:
– Client pays invoices 90 days late
– Supplier demands upfront payments due to past delays
– Bank rejects emergency loan
Result: Liquidation despite £1.2M in “paper profits.”
B. Debt Avalanches – When Borrowing Backfires
- Case Study: A fast-growing e-commerce firm takes on high-interest debt to fund inventory. Sales dip, interest compounds, and suddenly 60% of revenue services debt.
– Stat: 40% of UK SMEs struggle with unmanageable debt (Bank of England).
C. Currency & Commodity Swings
- Example: A UK bakery’s flour costs jump 30% after a wheat shortage. Contracts lock in prices — margins vanish overnight.
—
2. The Hidden Financial Risks That Compound Quietly
A. Customer Concentration Risk
- Scenario: A B2B software firm gets 70% of revenue from one client. When that client leaves, payroll can’t be met.
- Rule of Thumb: No single client should exceed 15–20% of revenue.
B. Supplier Dependency & Price Shocks
- Case Study: A car manufacturer relies on one battery supplier. When shortages hit, production stalls for 3 months → £9M loss.
C. Fraud & Financial Mismanagement
- Stat: UK businesses lose £137B yearly to fraud, waste, and accounting errors (PwC).
- Example: A finance director “cooks the books” — investors pull out when the truth surfaces.
—
3. The Strategic Fallout: When Financial Risks Spiral
A. Credit Downgrades & Banking Nightmares
- Example: A once-stable firm misses a loan covenant — interest rates spike 5%, lines of credit freeze.
B. Investor Panic & Equity Crashes
- Case Study: A tech startup’s burn rate exceeds projections — VCs demand emergency restructuring, slashing valuation by 50%.
C. Employee Exodus (When Paychecks Bounce)
- Stat: 78% of employees leave within 6 months of payroll issues (CIPD).
—
4. The Ultimate Cost: Bankruptcy Dominoes
A. The “Profitable But Insolvent” Paradox
How It Happens:
1. Big contracts signed → revenue looks strong
2. Clients pay late → cash dries up
3. Suppliers demand payment → no money for salaries/tax
4. HMRC forces liquidation despite “growth.”
B. The Carillion Effect (Again)
- £7B collapse triggered by:
– Aggressive accounting
– Reliance on unsustainable contracts
– No cash buffer for delays
—
5. The Bottom Line: Quantifying Financial Risks

Key Insight: Financial risks don’t just reduce profits — they erase businesses in weeks.
—
More from BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub : How to Fix It
We explore real-world financial risk strategies, including:
- The 13-week cash flow rule (used by turnaround experts)
- How to renegotiate debt before it’s too late
- Building a “war chest” for crises
Actionable Task: Run a “stress test” on your cash flow: What if 2 clients pay 60 days late?
—
Chapter 5: Cyber Risks – The Invisible Threat That Could Bankrupt Your Business by Breakfast
Introduction: The Digital Time Bomb Ticking in Your Business
Imagine arriving at work to find:
- Your customer database on the dark web
- Fraudsters draining £250,000 from your account
- Ransomware locking every file until you pay Bitcoin
This isn’t a movie plot — it’s Monday morning for thousands of UK businesses. Cyber risks don’t just steal data; they extort cash, destroy reputations, and trigger regulatory hell. And here’s the worst part: Most victims never see it coming until the damage is done.
—
1. The Direct Costs: What Happens When Cybercrime Hits
A. Ransomware: The Digital Kidnapping Epidemic
- 2023 Reality: A UK construction firm’s blueprints, invoices, and payroll systems encrypted. Hackers demand £120,000 to unlock files.
- Stat: 73% of UK businesses hit by ransomware in 2023 (NCSC).
- Brutal Truth: Paying doesn’t guarantee recovery — 32% never get full data back (Sophos).
B. Data Breaches: When Your Customers Become Victims
- Case Study: A mid-sized retailer’s poorly secured e-commerce platform leaks 380,000 credit cards.
- £500,000 GDPR fine
- £1.2M in fraud reimbursements
- 22% customer churn
- Stat: Average UK data breach cost: £3.4 million (IBM).
C. Business Email Compromise (BEC): The Silent Heist
- How It Works: A hacker impersonates your CEO, emails finance: “Urgent: Transfer £80k to new supplier.”
- UK Losses: £1.3 billion stolen via BEC in 2023 (UK Finance).
—
2. The Hidden Costs That Cripple You Later
A. Reputation Freefall & Customer Exodus
- After a breach:
– 58% of customers avoid breached brands (Verizon)
– Recovery Cost: 3–5X more on marketing to rebuild trust
B. Operational Paralysis
- Example: A law firm’s servers go down for 72 hours post-attack. £350k in billable hours lost + client lawsuits.
C. Insurance Nightmares
- Post-Claim Realities:
– Premiums triple
– Mandatory audits drain management time
– Some policies simply won’t renew
—
3. The Strategic Fallout: Long-Term Business Damage
A. Lost Contracts & Blacklisting
- Government/Corporate Tenders Now Demand:
– Cyber Essentials Certification (missing? Disqualified automatically)
– Proof of incident response plans
B. Investor Flight
- Startup Killer: A fintech’s pre-IPO breach scares off VCs, slashing valuation by 60%.
C. Director Liability (Yes, You Can Go to Jail)
- UK Law: Under GDPR & NIS Directive, negligent executives face fines up to £17.5M or 4% of global revenue — plus disqualification.
—
4. Why Cyber Risks Are Worse Than You Think
A. It’s Not Just “Big Targets”
- 61% of UK attacks hit SMEs (Verizon) — hackers bet they’re unprepared.
B. Remote Work = 300% More Attack Surfaces
- Example: An employee’s compromised home laptop gives hackers access to your entire CRM.
C. AI-Powered Attacks Are Here
- New Threat: Deepfake audio of your CFO “calling” finance to wire funds.
—
5. The Bottom Line: Cyber Risk Costs

Key Insight: Cyber risks aren’t an “IT problem” — they’re an existential business threat.
—
More from BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub : How to Fight Back
We will explore real-world cyber defenses, including:
- The 5-step SME ransomware shield (costs <£5k/year)
– How to trick hackers into avoiding you (attackers prefer easy targets)
– Turning employees into human firewalls
Actionable Task: Run this free test now: [Have I Been Pwned](https://haveibeenpwned.com/) to check if your work emails are already in hacker databases.
—
Chapter 6: Human Risks – When Your Greatest Asset Becomes Your Biggest Liability
Introduction: The Enemy Inside Your Walls
Your employees can either be your strongest defence — or your weakest link. Negligence, disengagement, and malicious actions cost UK businesses £30 billion annually (ACAS). This chapter exposes how poor people risk management leads to:
– Catastrophic errors
– Culture collapse
– Regulatory disasters
– Fraud epidemics
And why traditional HR policies fail to prevent 89% of these risks (PwC).
—
1. The Obvious (But Ignored) Human Risks
A. The High Cost of Disengagement
- Example: A retail chain’s apathetic staff miss 40% of shoplifting incidents —costing £220,000/year in stolen stock.
- Stat: Disengaged employees are 450% more likely to cause operational errors (Gallup).
B. Turnover Tsunamis
- Case Study: A tech firm’s toxic culture drives out 7 senior engineers in 6 months — delaying a £2M product launch by 11 months.
- Replacement Cost: Up to 2X annual salary per lost employee (Oxford Economics).
C. Training Gaps That Become Legal Nightmares
- Reality Check: A warehouse worker badly operates a forklift, causing £80k in damages + HSE fines—because “training was just a 10-minute video.”
—
2. The Hidden (But More Dangerous) Human Risks
A. Insider Threats: When Employees Attack
- Shocking Stat: 58% of data breaches involve insiders (Verizon).
- Methods:
– The Malicious: IT admin sells customer data (£50k on dark web)
– The Careless: Accountant emails payroll files to personal Gmail
B. Culture Risks: How Toxicity Spreads
- Example: A sales team’s “win at all costs” mentality leads to fraudulent client promises — £600k in lawsuits + FCA investigation.
C. Leadership Blind Spots
- CEO Overconfidence: Ignoring team warnings about a flawed expansion → £3M write-off.
- Stat: 82% of business failures trace back to poor leadership decisions (KPMG).
—
3. The Strategic Fallout: When People Risks Sink Companies
A. The Volkswagen Emissions Scandal
- Root Cause: A culture where “nobody dared question” fraudulent engineering.
– Cost: €32 billion in fines/losses + permanent brand damage.
B. The Barclays CEO Scandal
- How It Happened: Leadership’s obsession with “star hires” led to unchecked bullying — triggering £1M fines + investor revolt.
C. The Everyday SME Killer
- Scenario: Your “trusted” bookkeeper embezzles £150k over 3 years — exposed only during a tax audit.
—
4. Why Traditional Approaches Fail
- Annual compliance training? 86% of employees forget it within 30 days (MIT).
- “Hotline whistleblowing”? 62% of staff fear retaliation (EY).
- Top-down policies? Frontline teams see them as “head office nonsense.”
—
5. The Bottom Line: Quantifying People Risks
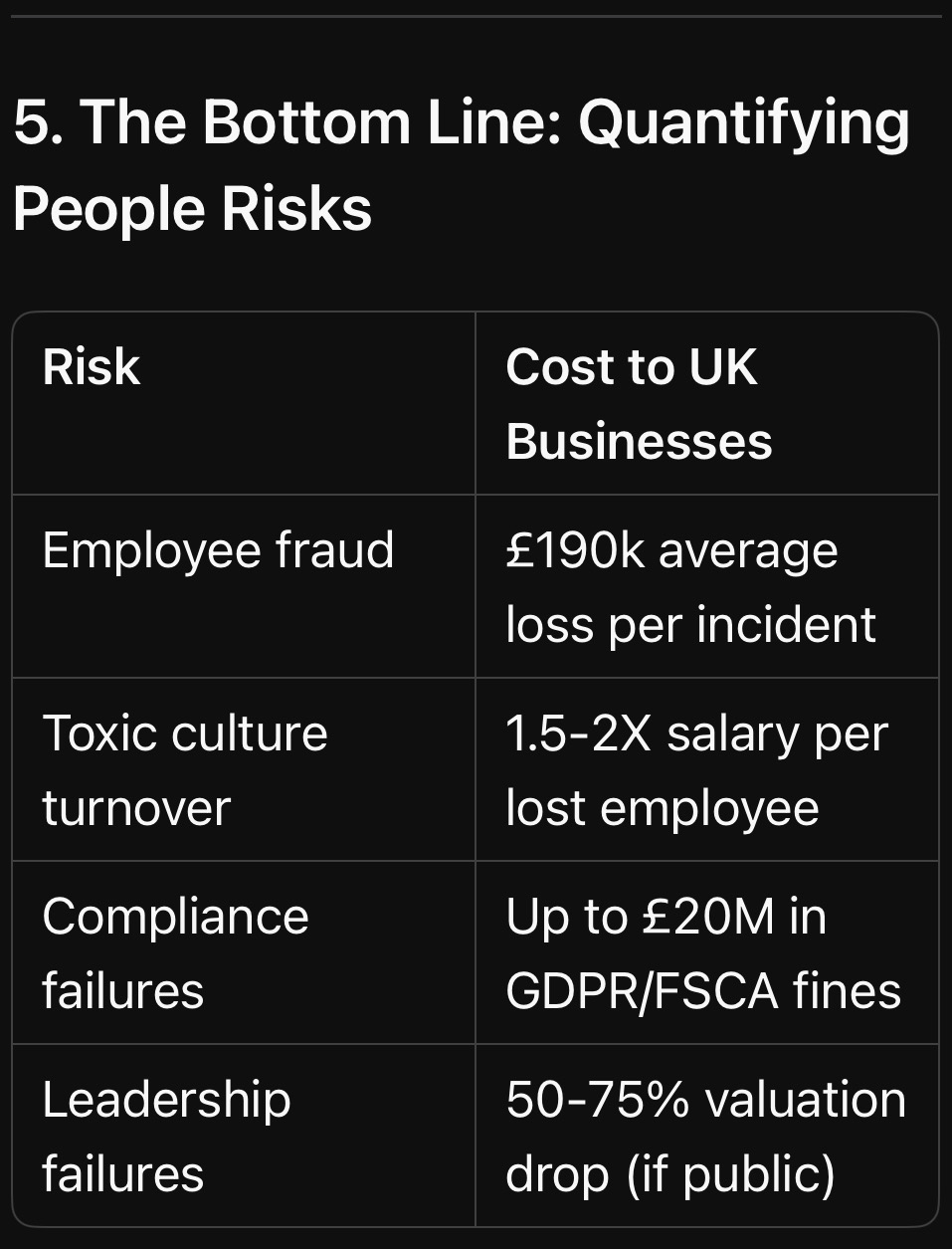
Key Insight: Your employees create or destroy value daily — often without realising it.
—
More from BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub : How to Transform Human Risk into Advantage
We explore battle-tested solutions, including:
- The “Psychological Safety” hack
- How to spot insider threats before they strike
- Turning compliance into competitive edge
Actionable Task: Run a 5-minute “risk culture pulse check” with your team this week: “What’s one process you think could fail catastrophically?”
—
Chapter 7: Supply Chain Risks – The Fragile Web That Could Strangle Your Business Overnight
Introduction: Your Business Is Only as Strong as Its Weakest Supplier
A single delayed shipment. One insolvent vendor. A geopolitical shockwave. Suddenly, your production line stops, customers revolt, and cash flow evaporates.
Supply chain risks aren’t hypothetical—they’re profit-killing realities:
- 43% of UK companies faced severe supply disruptions in 2023 (CIPS)
- 1 in 5 SMEs nearly collapsed due to supplier failures (FSB)
- The average disruption costs £225k (Lloyd’s of London)
This chapter exposes how vulnerable your supply chain really is — and why “just-in-time” has become “just-too-late” for thousands of businesses.
—
1. The Visible Supply Chain Killers
A. Supplier Collapses – The Domino Effect
- 2023 Reality: A key automotive parts supplier goes bankrupt → 3 UK car plants idle for 6 weeks → £180M in lost production.
- Stat: 58% of businesses have no backup for critical suppliers (Deloitte).
B. Logistics Breakdowns
- Red Sea Crisis Fallout: Shipping costs spike 400%, delays stretch to 8 weeks → retailers miss entire seasonal sales windows.
- Brexit Hangover: 27% of UK manufacturers still face customs delays (Make UK).
C. Price Volatility & Extortion
- Example: A bakery’s flour supplier doubles prices overnight due to war in Ukraine — contracts force them to absorb the cost.
—
2. The Hidden (But More Dangerous) Supply Chain Risks
A. Single-Point Failures
- Case Study: A pharma company relies on one Indian API supplier — FDA bans the factory → 2-year drug shortage.
B. Quality Failures That Slip Through
- Costly Reality: A construction firm’s “cheaper” Chinese steel fails safety tests → £1.2M in rework + penalty clauses.
C. Forced Labour & Compliance Bombshells
- US/Uyghur Forced Labor Act: Companies unknowingly using Xinjiang cotton face seized shipments + 20% tariffs.
—
3. The Strategic Fallout When Chains Break
A. Customer Mass Exodus
- Example: An electronics retailer’s Christmas stock arrives January 5th → 35% return rate + brand hashtag trends in anger.
B. Cash Flow Cardiac Arrest
How It Happens:
- Prepay for inventory → delays eat working capital
- Miss delivery deadlines → penalty payments
- Banks freeze credit lines
C. The Reputation Reckoning
- Boohoo’s Leicester Scandal: £1B market cap wiped out after slave labour exposé.
—
4. Why Traditional “Solutions” Fail
- Dual Sourcing? Most secondary suppliers use the same raw material sources.
- Bigger Inventories? Eats cash flow + risks obsolescence.
- Longer Contracts? Locks you into outdated pricing.
—
5. The Bottom Line: Supply Chain Risk Costs
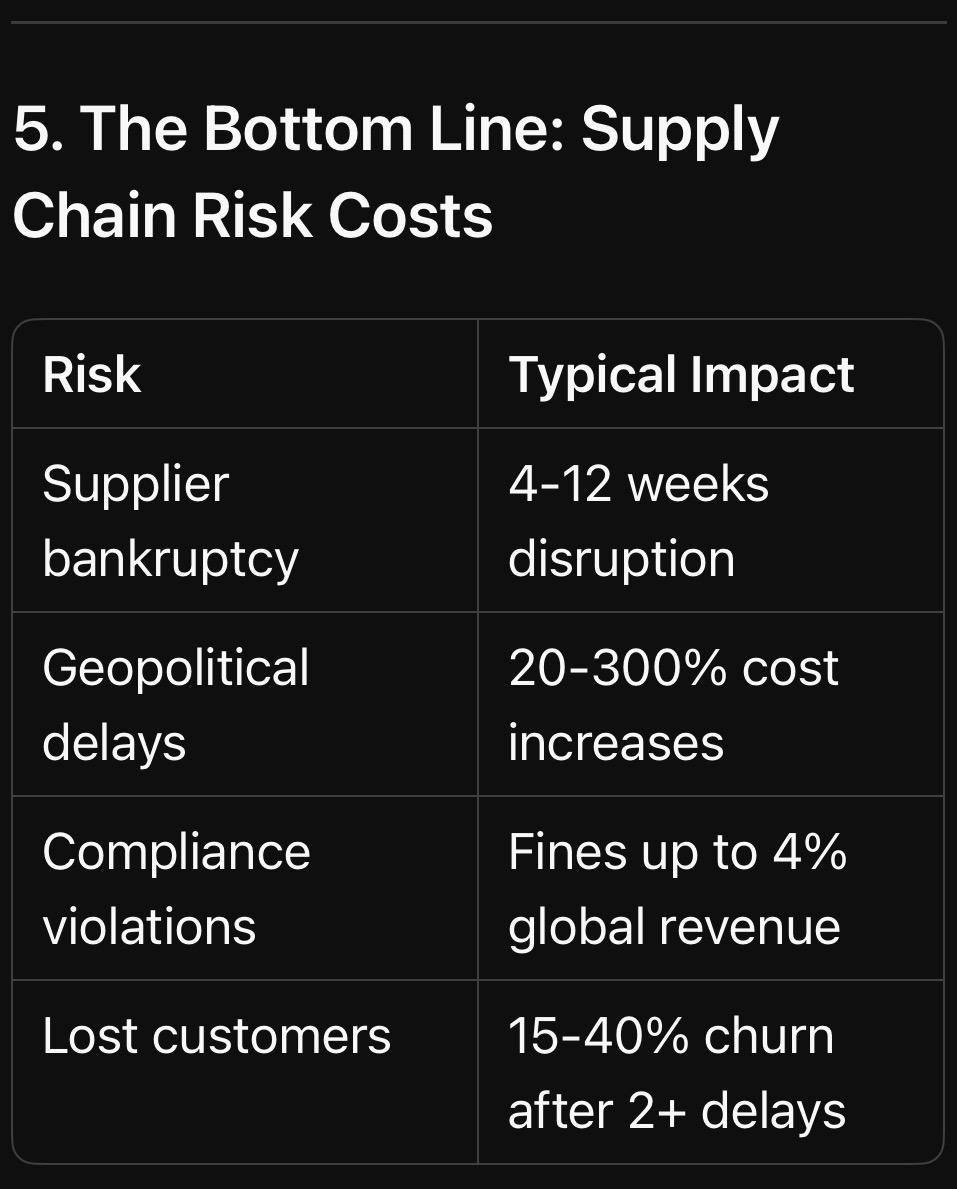
Key Insight: Supply chains have become the ultimate leverage point — for your competitors or your downfall.
—
More from BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub : How to Build an Unbreakable Supply Chain
We explore wartime-tested strategies, including:
- The “3D Supplier Mapping” trick (used by Special Forces logisticians)
- How to turn suppliers into partners (not adversaries)
- When to nearshore/onshore without bankrupting yourself
Actionable Task: Identify one “critical” supplier you couldn’t operate without. How would you survive if they vanished tomorrow?
—
Chapter 8: Reputational Risks – When Trust Collapses Faster Than Your Share Price
Introduction: The 24-Hour Business Execution
A single tweet. One viral video. A disgruntled employee’s LinkedIn post. In today’s digital wildfire, your hard-earned reputation can evaporate before your crisis team finishes their first coffee.
The brutal reality:
- 87% of consumers will abandon a brand after a reputation crisis (YouGov)
- It takes 4-7 years to build trust but just 4 bad days to destroy it (Edelman Trust Barometer)
- 65% of a company’s market value is tied to intangible assets like reputation (Ocean Tomo)
This isn’t about PR spin – it’s about preventing the preventable and surviving the unpredictable.
—
1. The Obvious Reputation Killers
A. Social Media Firestorms
- Case Study: A restaurant manager’s racist comment caught on video → 300,000 angry tweets in 48 hours → permanent 40% revenue drop
- Stat: Viral crises spread 20x faster than management can respond (MIT Sloan)
B. Executive Scandals
- The P&G CEO Effect: A $375 billion company lost $40B in market cap in days after CEO’s inappropriate relationship surfaced
C. Product Failures Gone Viral
- Samsung Note 7 Disaster: Exploding phones cost $17B + 3-year brand recovery
—
2. The Hidden Reputation Risks
A. “Slow Burn” Erosion
- Example: A bank’s 1,200 small complaints/month on Trustpilot → unnoticed 2% annual customer attrition → £200M revenue gone in 5 years
B. Guilt by Association
- Reality: Your 3rd-tier supplier’s child labour scandal becomes YOUR front-page crisis
C. Algorithmic Assassination
- Google’s Autocomplete Effect: “YourBrand + lawsuit/scam/fraud” suggestions deter 63% of potential customers (Moz)
—
3. The Financial Fallout

The Domino Effect:
1. Crisis hits → 2. Customers leave → 3. Talent flees → 4. Investors panic → 5. Suppliers demand cash upfront
—
4. Why Traditional PR Fails
- “No comment” = “We’re guilty” in public perception
- Corporate-speak increases distrust by 41% (Edelman)
- Legal-first responses often worsen the crisis
—
5. The Survival Playbook (Preview)
More from BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub we will explore modern reputation armour, including:
- The “Dark Web Early Warning” system (catch crises before they explode)
- Turning employees into reputation ambassadors
- When to apologise vs. when to fight back
Actionable Task: Google “[Your Brand] + scandal” right now. What autocomplete suggestions appear?
—
Chapter 9: Climate Risks – The Existential Threat That’s Already Costing Your Business
Introduction: Your Business Is on the Frontlines of the Climate Crisis
Climate change isn’t a distant threat — it’s eroding profits, disrupting supply chains, and rewriting industry rules right now. In 2024 alone, climate disasters caused $2 trillion in global losses, with businesses absorbing the brunt through:
- Operational shutdowns (e.g., factories flooded, data centres overheated
- Soaring insurance premiums (up 300% in high-risk zones)
- Regulatory penalties (e.g., non-compliance with carbon disclosure rules)
This chapter exposes the hidden costs of climate risks — and why most companies are dangerously unprepared.
—
1. The Two Faces of Climate Risk
A. Physical Risks: When Nature Attacks
1. Acute Disasters:
– Example: Hurricane Helene (2024) caused $225B in damages, disrupting microchip supplies by destroying a key quartz supplier .
– Stat: Severe weather events now cost businesses $560–610B yearly in asset losses .
2. Chronic Pressures:
– Heatwaves reduce worker productivity by 15–20% in sectors like construction and agriculture .
– Droughts forced a UK beverage company to halt production for 6 weeks due to water shortages .
B. Transition Risks: The Legal and Market Backlash
1. Policy Shocks:
– Carbon taxes could erase 20% of profits for high-emission firms by 2030 .
– Example: EU’s Carbon Border Tax added 10–20% costs for non-compliant imports .
2. Reputation Fallout:
– 75% of consumers boycott brands with poor sustainability records .
– Investor Flight: ESG-backlash aside, 90% of Fortune 500 firms now face shareholder climate lawsuits .
—
2. The Hidden Costs You’re Not Tracking
A. Supply Chain Domino Effects
- Case Study: Floods in Thailand (2023) disrupted 40% of global hard drive production → tech firms lost $20B+
- Stat: 73% of companies admit their supply chains are “highly vulnerable” to climate shocks .
B. Workforce Crises
- Heat Stress: UK warehouses saw 30% more sick days during 2024’s record summer .
- Talent Drain: 67% of Gen Z employees reject jobs at firms with weak climate policies .
C. Stranded Assets
- Example: Oil companies wrote off $300B in reserves as “unburnable” due to net-zero policies.
- Projection: 20% of commercial real estate will be uninsurable by 2030 .
—
3. Why Businesses Underestimate Climate Risks
- “It Won’t Happen Here” Bias: 80% of SMEs lack climate contingency plans .
- Short-Termism: Only 20% of executives prioritise climate risks over quarterly targets.
- Data Gaps: Most firms rely on “best guess” estimates for emissions and vulnerabilities .
—
4. The Bottom Line: Quantifying the Threat
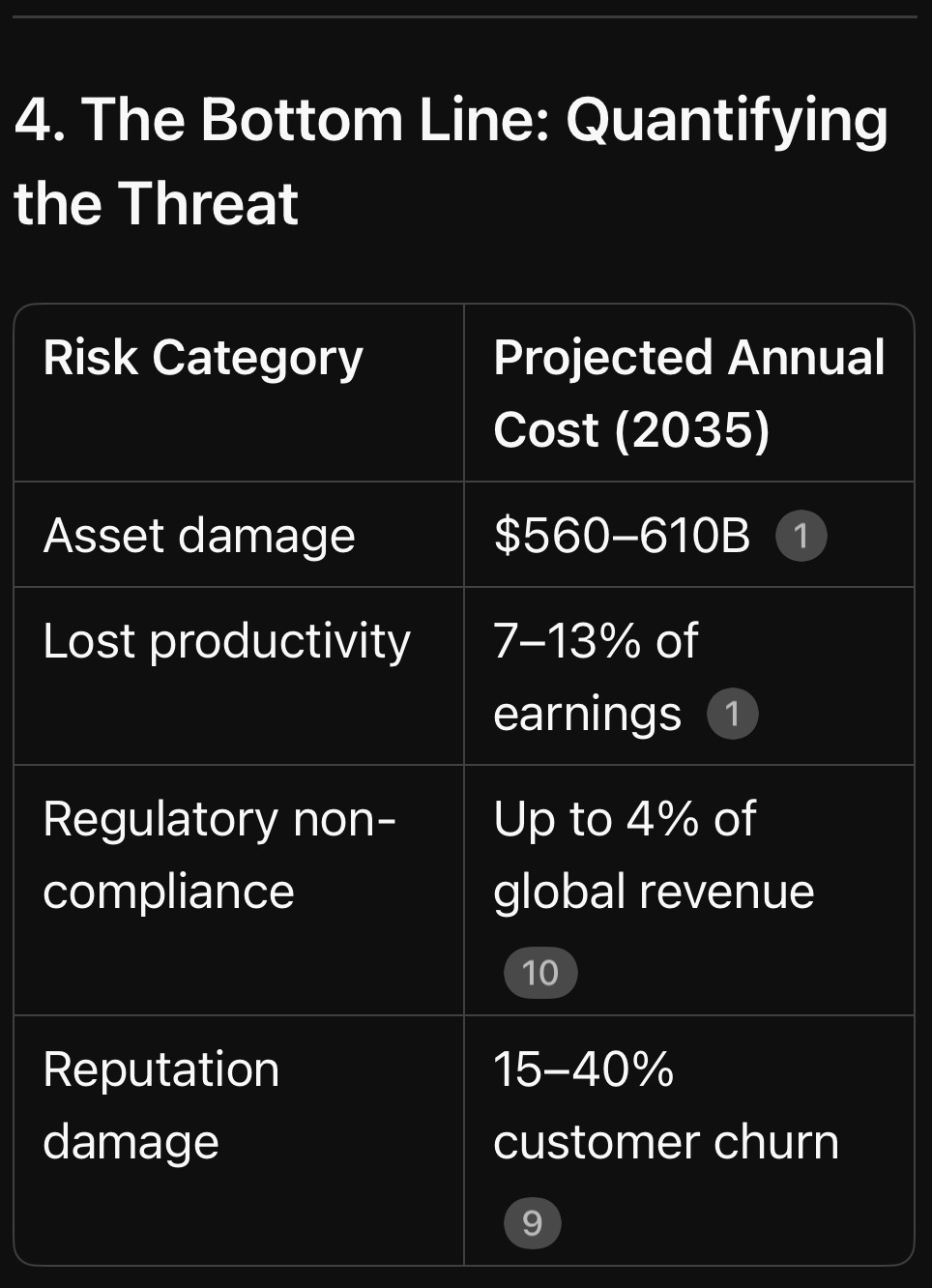
Key Insight: Climate risks are profit killers — not just “ESG checkboxes.”
—
More from BusinessRiskTV Business Experts Hub : How to Fight Back
We will explore actionable climate resilience strategies, including:
- The “3D Supply Chain Mapping” tactic (used by Special Forces logisticians)
- How to turn carbon cuts into tax savings
- AI-powered climate forecasting tools
Actionable Task: Run a 5-minute vulnerability scan: Which single climate threat (e.g., flood, heatwave) could shut down your operations for 48 hours?
—
*Sources: World Economic Forum , Allianz , Beazley , Optera , EPA *
Chapter 10: 12 Actionable Solutions to Transform Risk into Competitive Advantage
Introduction: Risk Management Isn’t About Survival—It’s About Dominance
The most profitable companies don’t just avoid risks — they weaponise them. Toyota’s supply chain resilience made it the #1 automaker during the chip shortage. Amazon turned cybersecurity into a $35B AWS profit centre.
This chapter delivers 12 battle-tested solutions to stop losing money and start outpacing competitors.
—
Solution 1: The “Risk Ownership” Culture Hack
- Problem: Employees see risk as “management’s problem.”
- Fix:
– Tie 10-15% of bonuses to risk KPIs (e.g., near-miss reports, compliance audits)
– Example: A logistics firm reduced warehouse injuries by 62% after adding safety metrics to performance reviews
Action Step: This week, have each department identify one preventable risk they’ll now “own.”
—
Solution 2: The 5-Minute Daily Risk Radar
- Problem: Monthly reports miss emerging threats.
- Fix:
– Daily 5-minute standups on: - Top 3 operational vulnerabilities (e.g., server capacity, inventory levels)
- Weak signals (e.g., supplier payment delays, social media complaints)
- Case Study: A manufacturer caught a critical component shortage 3 weeks early by tracking supplier lead times daily
**Template:**
“`
[ ] Key risk #1 status
[ ] New threat detected
[ ] Mitigation action
“`
—
Solution 3: Cyber “Human Firewall” Training That Works
- Problem: Boring compliance training fails.
- Fix:
- Monthly simulated phishing with “hacked” employees retaking interactive VR training
Result: One law firm reduced click-through rates from 28% to 3% in 6 months
Free Tool: Use CanIPhish for automated simulations
—
Solution 4: The 13-Week Cash Flow War Chest
- Problem: Companies die from cash flow gaps, not lack of profit.
- Fix:
1. Map all cash inflows/outflows week-by-week
2. Identify 3 survival levers (e.g., delayed payables, early collections)
3. Stress test with:
– 30% sales drop
– 60-day client payment delays
Example: A restaurant chain survived COVID by pre-negotiating 90-day rent deferrals before lockdowns
—
Solution 5: Supplier “X-Ray” Audits
- Problem: 4th-tier suppliers can bankrupt you.
- Fix:
– Demand blockchain-tracked materials for critical inputs
– Red Team Test: Randomly delay payments to check supplier liquidity
– Stat: Firms with mapped supply chains recover 9x faster from disruptions
—
Solution 6: AI-Powered Risk Forecasting
Toolkit:
- Climate: Cervest (predict asset flooding)
- Cyber: Darktrace (autonomous threat detection)
- Financial: Simudyne (stress test scenarios)
ROI Example: A insurer cut claims by 22% using flood prediction AI
—
Solution 7: The “Pre-Mortem” Strategy Session
- Problem: Executives ignore failure scenarios.
- Fix: Before decisions:
1. Imagine the project has failed catastrophically
2. Brainstorm exactly why
3. Build safeguards
Case Study: Boeing’s 737 Max crashes could’ve been prevented by this method
—
Solution 8: Embedded Risk Officers
Innovation: Place risk champions in:
– R&D teams (kill flawed prototypes early)
– Sales (flag unrealistic client promises)
– Result: A pharma firm avoided $200M in FDA fines by catching compliance gaps during drug development
—
Solution 9: Dynamic Risk Scoring
Tool: Custom risk dashboards weighting:
– Probability (1–10)
– Impact (£)
– Velocity (how fast threat is growing)
– Example: A bank auto-prioritises risks scoring >£500k impact
—
Solution 10: The “Unthinkable” Drill
Annual Exercise: Simulate:
– CEO arrested
– HQ destroyed
– Key Result: BrewDog survived a ransomware attack because they’d practiced IT failovers quarterly
—
Solution 11: Turn Risk Into Revenue
Examples:
– Tesla sells carbon credits ($1.8B in 2023)
– Maersk’s green shipping premiums command 20% price hikes
—
Solution 12: The Risk Transparency Report
Innovation: Publicly share:
– Top 5 near-misses
– Lessons learned
– Outcome: Unilever’s radical transparency boosted investor trust post-crisis
—
Final Action: Your 30-Day Risk Revolution
1. Pick 3 solutions to implement now
2. Assign owners/deadlines
3. Report results in next quarter’s board pack
Remember: Risk mastery isn’t about fear — it’s about freedom to outmaneuver competitors.
—
Need help prioritising solutions for your industry? Reply with your sector for tailored advice
Get help to protect and grow your business faster with BusinessRiskTV
Find out more about Business Risk Management Club
Subscribe for free business risk management tips risk reviews and cost reduction ideas
Connect with us for free risk alerts and risk management newsletters
Read more business risk management articles and view videos for free
Connect with us for free risk management articles and video releases
Enterprise Risk Management Magazine BusinessRiskTV ERM Magazine
Read more risk management strategies articles and view videos :
1. “How poor risk management increases business costs and reduces profits”
2. “Operational risk failures that hurt profitability and how to fix them”
3. “Why businesses fail due to unmanaged risks and how to survive”
4. “Employee engagement strategies for better risk management in business”
5. “Hidden costs of ignoring risk management in small and medium enterprises”
Relevant hashtags :
1. #UKBusinessRisk
2. #ProfitProtection
3. #SMEsAtRisk
4. #BusinessSurvivalGuide
5. #LeadershipRisk
How poor risk management increases business costs and reduces profits